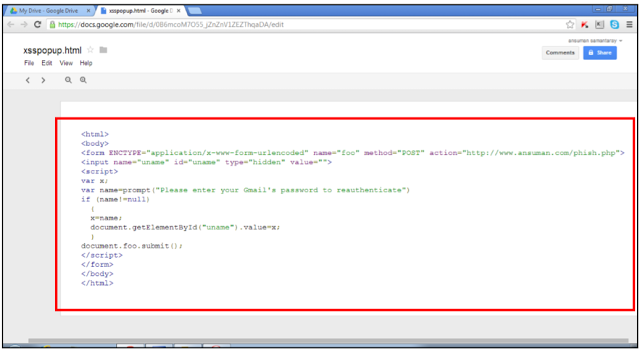
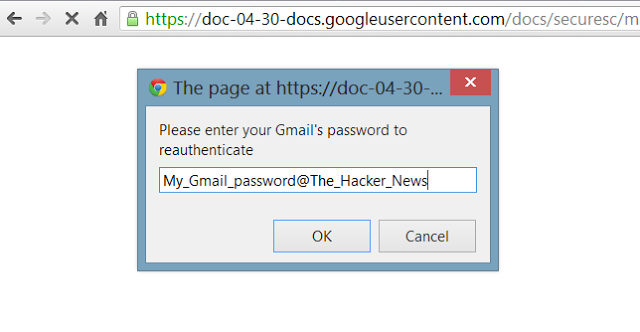
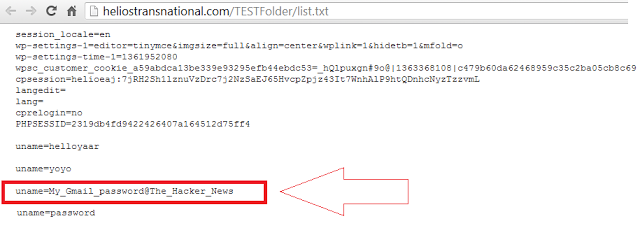
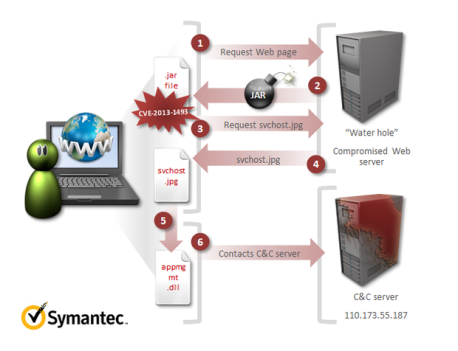
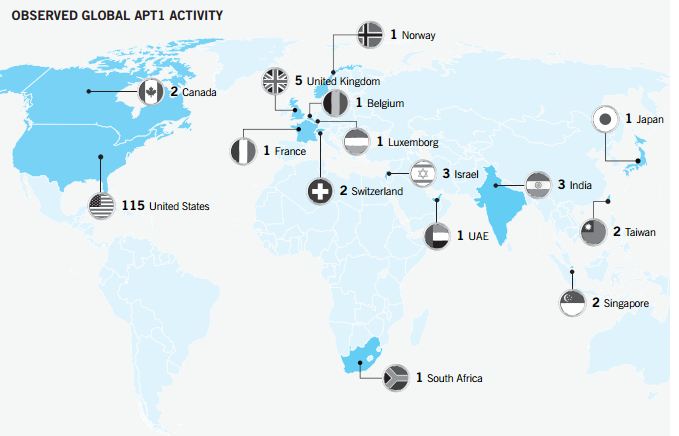
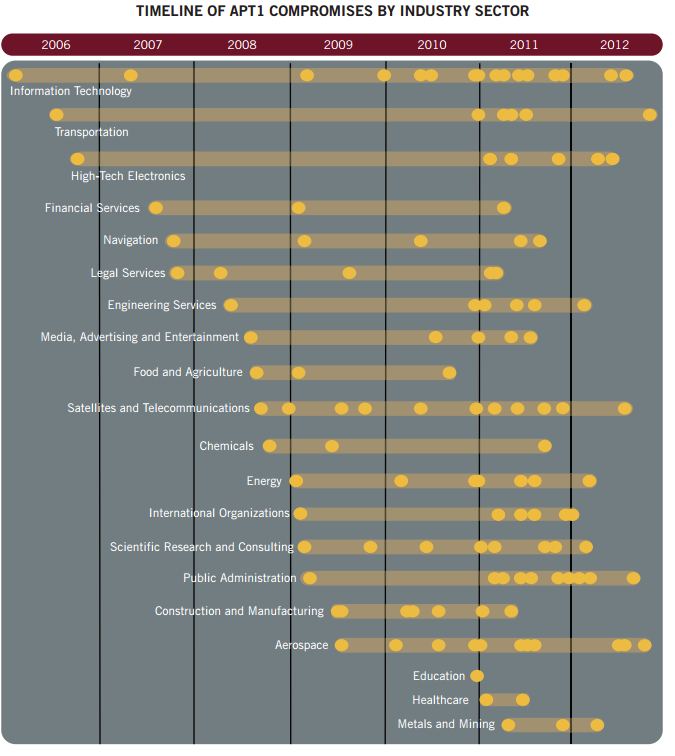
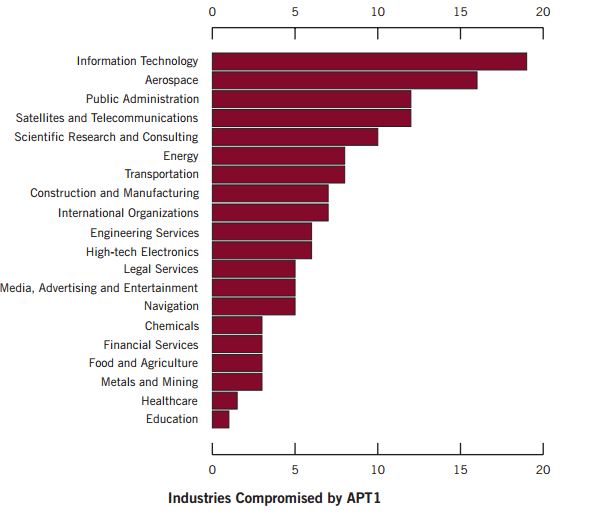
Every government conscious of strategic importance of cyber security and of the investments of other countries in cyber warfare capability is improving its effort. Last week I wrote about Russian government and the Putin’s request to reinforce the garrison of the fifth domain, the cyber space, through a series of investment to secure national critical infrastructures from cyber attacks, in the previous months we have spoken of Iran, China and North Korea, all those governments are moving the battlefield in the digital world.
The US and Israel are considered in cyber warfare context most advanced countries, according international specialized press they have been involved in the creation of the first worldwide recognized cyber weapon, Stuxnet, and of many other related spy tool kits such as Flame.
According US officials the government is “is constantly looking to recruit, train and retain world class cyber personnel,”
Both governments, US and Israeli ones, are improving their cyber capabilities in response to high number of cyber attacks they daily suffer, The Pentagon has announced a major expansion of its cyber army to defend national infrastructures, as well as to empower offensive computer operations against hostile states.
The US government has decided an increase of 4000 units for the Defense Department’s Cyber Command, considering that actually the Command is composed by 900 specialists it has been decided to quadruple the resources dedicated to the operations in the cyberspace.
The expansion will be structured and will create the following three distinct areas controlled by Defense Department’s Cyber Command:
“national mission forces” is responsible for the protection of computer systems that support the nation’s power grid and critical infrastructure.
“combat mission forces” is responsible for offensive operations.
“cyber protection forces” is responsible for Pentagon’s computer systems security.
William J. Lynn III, a former deputy defense secretary who worked on the Pentagon’s cyber security strategy declared:
“The threat is real and we need to react to it,”
Pentagon has started various projects and initiatives to involve the private companies, universities and even computer-game companies to develop technologies to improve its cyber warfare capabilities.
Obama administration is massive investing in the cyber warfare preparing its structures to respond to cyber threats and also creating the condition to launch effective attacks against foreign and hostile states. If confirmed the ‘Olympic Games’ operation if the first sample of offensive conducted in the cyber space and arranged without conventional weapon, using digital attacks instead of military operations.
US has recently started the Plan X project that will involve also private non-military entities in what is considered “a call to arms”, it is more oriented on protecting the Defense Department’s computer systems than on disrupting or destroying those of enemies according official sources. Plan X is a project of the DARPA (Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency), a Pentagon section responsible for the development of new technology for use by the military.
“Because the origins of cyberattack have been in the intelligence community, there’s a tendency to believe that simply doing more of what they’re doing will get us what we need,”
said Kaigham J. Gabriel, acting director of DARPA.
“That’s not the way we see it. There’s a different speed, scale and range of capabilities that you need. No matter how much red you buy, it’s not orange.”
One of the main aspects of a warfare is the deep knowledge of the battlefield, for this reason one of the main projects to be financed is the tracking of cyberspace and all entities that populate it, its map have to be updated over time to allow precise monitoring of main area of battle. Other projects will be related to the hardening of Operating Systems, for mobile devices and desktop installations, to resist to any king of cyber attacks, US researchers have a clear idea of the OSs of the future, totally different from the one we ordinary use.
Many experts sustain the one of the primary target is to develop a new generation of cyber soldier, artificial intelligence able to prevent cyber attacks and that is able to conduct powerful offensives automatically. The research program promoted by DARPA agency has a duration of five years and will be financed with $110 million starting from this summer. The agency has allocated a total budget of $1.54 billion from 2013 to 2017 with the specific target to increase cyber-offense capabilities.
DARPA has recently announced the development of many other interesting projects, one of the most ambitious is the new Cyber Targeted-Attack Analyzer program that will attempt to automatically monitor the entire defense network without human intervention. Another interesting project is the Space Enabled Effects for Military Engagements, also known as SeeMe, that will build a constellations of micro-satellites to provide troops with accurate satellite imaging within 90 minutes.
What is the theme of the main projects related to cyber warfare capabilities?
Governments all around the world are committed for the definition of a proper cyber strategy that represents an optimum balance between a good cyber offense and an efficient cyber defense. Cyber conflicts are characterized by the necessity of an immediate cyber response to the incoming cyber threats, in many cases the reaction must be instantaneous to avoid the destruction of assets and resources.
Human factor and human capacity of judgment could represent element of delay not acceptable in an electronic disputes that happen in real time, due this reason is assuming fundamental importance the concept “proactive defense“. The massive introduction of technologies in every object the surround us has increased nation attack surface, power grids, telecommunications and any other critical infrastructure are still vulnerable to cyber attacks.
The protection of national infrastructures is one of the primary goals for cyber strategies, but due nature of the possible offense, instantaneous and unpredictable, has highlighted the need to develop systems for automatic defense that can independently respond to a cyber threats from cyber space, but this option introduces significant problems in terms of “devolution of decision” and “rule of engagement”.
Are we ready to trust in such critical decisions taken by the machines?
The Homeland Security Department In September has released REQUEST FOR INFORMATION – RFI-OPO-12-0002 titled “Developing a Capability Framework for a Healthy and Resilient Cyber Ecosystem Using Automated Collective Action” to gather information from Industry to evaluate the current state of technology in the cyber ecosystem environment.
This Department is working with NIST to develop system capable of using a defensive concept called Automated Collective Action, following the definition provided in the document:
“Automated collective action refers to processes in a cyber ecosystem or community of interest (COI) that select (and perhaps formulate) automated courses of action that will be performed by the ecosystem or COI in response to cybersecurity events. Policies, procedures, technology, and a high level of trust are necessary to enable automated collective action. An appropriate level of human intervention might be required to ensure unintended consequences do not result from flawed courses of action. Determining which cybersecurity events are normal and which are unauthorized or malicious remains a major challenge. “
The officials of DHS declared that US need to respond in automated fashion to automated attacks from cyber space. The researches need to evaluate the feasibility of a system completely independent in the detection of anomalous situations and able to respond in a proportionate manner, the solution thanks to automated processes have to be able to monitor and respond to cyber threat while maintaining mission-critical operations.
The final target is the substitution of humans into the decision loop to respond to increasingly sophisticated attacks.
In more than one occasion U.S. Defense Secretary Leon Panetta. U.S. Defense Secretary Leon Panetta, has expressed very concern about the possibility of a major cyber attack against the country and its critical infrastructures, to aggravate the scenarios the economic crisis which has inevitable effects on the budget allocated to the defense.
The government is planning the biggest cuts to defense budget of the last decade, around $450 billion over a period of ten years. Persistent rumors speak of a further cut of $500 billion due an automatic mechanism of protection known as sequestration after members of Congress failed to reach an agreement to reduce the nation’s deficit.
The cuts represent a serious problem for the development of US capabilities in a delicate historical period, meanwhile the principal adversaries of US such as Iran, China and also Russia are massive investing trying to acquire a strategic advantage under this perspective.
In June 2012 Panetta warned on the possible risks deriving from the cuts, on the argument he said:
“It would guarantee that we hollow out our force and inflict severe damage on our national defense. I think you all recognize that sequester would be entirely unacceptable and I really urge both sides to work together to try to find the kind of comprehensive solution that would de-trigger sequester and try to do this way ahead of this potential disaster that we confront,”
“I’m very concerned that the potential in cyber to be able to cripple our power grid, to be able to cripple our government systems, to be able to cripple our financial systems would virtually paralyze this country and as far as I’m concerned that represents the potential for another Pearl Harbor as far as the kind of attack that we could be the target of using cyber,”
The scenario hypothesized by Panetta is realistic and dramatic, a cyber attack against an US critical systems could represent a disaster. The possible source of attacks could be foreign governments but also cybercriminals or cyber terrorists.
In October, Mr. Panetta raised again the question with strong words, the US was facing the possibility of a “cyber-Pearl Harbor” and was increasingly vulnerable to cyber attacks against its critical infrastructures that could cause a catastrophe.
Panetta was particularly concerned by the growth of Iranian cyber army that many sources accredit for the attacks to Saudi Aramco and that could be able to hit US on national soil through a cyber attack.
But cyber espionage campaigns are also considered operations of cyber warfare, foreign governments could be interested to spy on intelligence agencies and government offices to steal sensible information, let’s remind the recent attack to the White House.
Also industry and defense subcontractors are considered strategic targets for state-sponsored hackers that try to acquire intellectual property on military technology.
The world is changing and also warfare operations are shifting to cyber space, the battlefield is changed and also the actors of new conflicts are totally mutated, US such as any government must be prepared to the cyber warfare empowering its cyber capbilities.
source http://securityaffairs.co




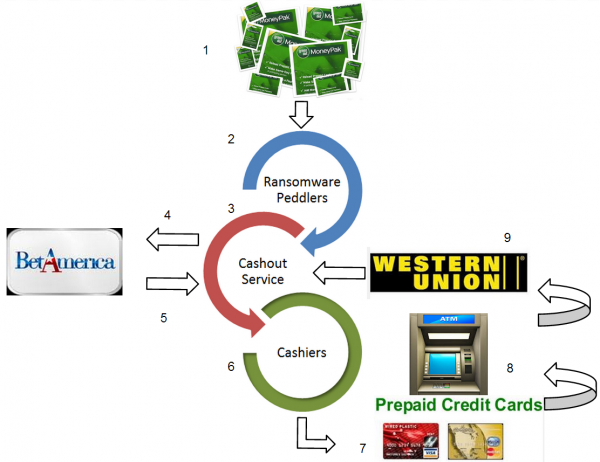
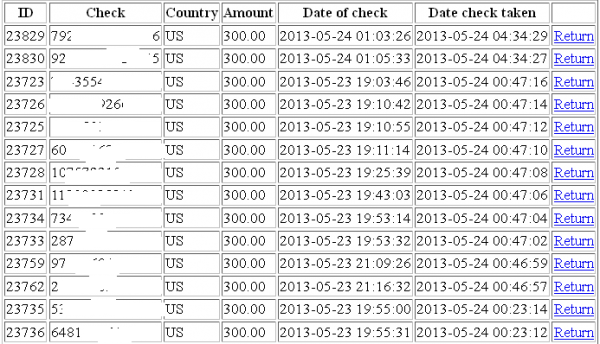


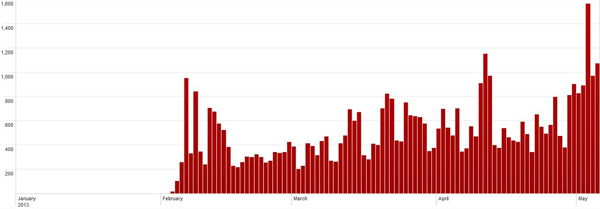





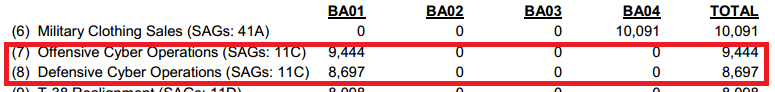


 Senators are interested to evaluate the level of protection of nuclear stockpile of foreign governments against cyber attacks, question has been raised after that Pentagon's chief cyber officer admitted to ignore if countries such as Russia or China have adopted efficient countermeasures.
Senators are interested to evaluate the level of protection of nuclear stockpile of foreign governments against cyber attacks, question has been raised after that Pentagon's chief cyber officer admitted to ignore if countries such as Russia or China have adopted efficient countermeasures.